Ruptured eardrum and perforated eardrum are commonly used to refer to a condition where there is a tear or hole in the thin tissue that separates the ear canal from the middle ear. Our eardrum helps us to hear and also serves as a protective partition to prevent water, dirt, and bacteria from getting into the middle ear.
Table of Contents
How Do I Know If I Have Ruptured My Eardrum?
If you have been using a sharp object in your ears to clean them, or accidently something has gone into your ear and you feel a sharp pain, the chances are that you have ruptured your eardrum. Ear discharge is another sign of a ruptured eardrum.
What Are The Ruptured Eardrum Symptoms?
Below are some of the signs of a ruptured eardrum.
- Severe ear pain
- Bloody discharge or pus-filled discharge
- Nausea
- Dizziness or Vertigo
- Ringing in the ears or Tinnitus
- Sudden hearing loss in the affected ear
Is A Ruptured Eardrum Painful?
If the ruptured eardrum is caused by a foreign object, you will feel a sharp pain. After some time, the pain may go away or subside to a tolerable level. Eardrum perforation caused by infection is not as painful and you may not realize it or feel mild discomfort.
What Does A Ruptured Eardrum Look Like?
Your eardrum or the tympanic membrane is a thin circular tissue located at the end of the ear canal. The average diameter of the eardrum or the tympanic membrane is around 10mm and the thickness is around 50–150 micrometers. (1 micrometer is equal to 0.001 millimeters)
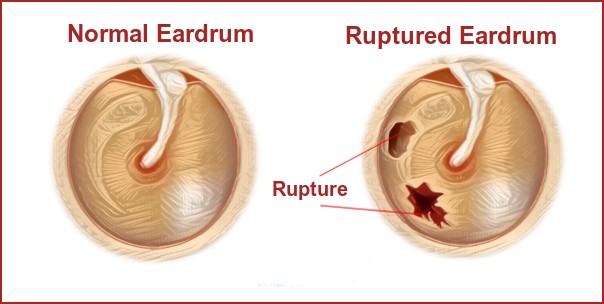
What Causes A Ruptured Eardrum?
Some of the common ruptured eardrum causes are:
- Middle ear infection
- An accident or injury to the eardrum
- Inserting a foreign object like a cotton bud deep into your ear
- Changes in pressure experienced while flying or scuba diving. (Ear barotrauma)
- Sudden loud noise or an explosion (Acoustic trauma)
f you have been suffering from an ear infection and notice a discharge that was not present earlier, it can be a sign of a ruptured eardrum.
If the eardrum perforation is because of a sharp object or aggressive use of cotton earbuds or Q tip, then you will notice blood in the ear discharge.
How Long Will A Ruptured Eardrum Leak?
Your ruptured eardrum will start healing or close by itself without any eardrum surgery in about two weeks’ time. Total healing takes around two months. The eardrum leakage will stop as the tear in the eardrum closes. If you do not notice any reduction in ear discharge after two weeks, it is advisable to see a doctor to explore other options.
What Does A Ruptured Eardrum Feel Like?
At times it is difficult to determine if the eardrum has ruptured as the sudden pain you experienced at the time of the rupture goes away and all you feel is a slight discomfort thereafter.
What To Do For A Ruptured Eardrum?
Visit a doctor and get your ears examined. The doctor will look into the ear using an otoscope to check for a tear or perforation. The doctor may recommend an audiometry test and tympanometry test to determine the extent of the hearing loss and the state of the eardrum.
An audiometry test determines the degree of hearing loss. A tympanometry test checks the response of the eardrum when pressure is applied.
How Long Does It Take A Ruptured Eardrum To Heal?
If the rupture or eardrum perforation is not very severe, the doctor may decide not to operate immediately. Generally, the ruptured eardrum healing time is two to three months.
What Are The Perforated Eardrum Treatment Options?
Initially, the doctor may prefer eardrum hole repair without surgery, in case the eardrum tear is big, then the doctor may suggest eardrum surgery.
Mostly the tear or perforation will close by itself as the eardrum tissue heals naturally. The doctor will prescribe antibiotic eardrops or oral antibiotics to prevent ear infections during the healing period.
If the eardrum rupture is not healing as expected, the doctor may decide to use a patch or tissue to seal the eardrum tear.
Patch Eardrum Surgery
Patch myringoplasty or patch eardrum surgery is a small procedure and usually takes about 15 minutes. The procedure involves covering the eardrum hole or perforation with a small piece of special paper or soluble gelatin.
The paper covers the eardrum hole and restores normal hearing and allows the hole to heal naturally. The paper dissolves after some time, however, this procedure is only suitable if the hole or eardrum tear is small.
If the eardrum rupture is not healing as expected or is slow in healing, the doctor may decide to use a tissue graft to seal the eardrum tear.
Tympanoplasty Surgery
In case the rupture is big and the chances of healing naturally are less, then the doctor may recommend surgical repair of the eardrum. The procedure is known as tympanoplasty.
What Is The Tympanoplasty Procedure?
The tympanoplasty surgery is done in steps, the tympanoplasty steps are described briefly:
Tympanoplasty Steps
Tympanoplasty is done under general anesthesia. The doctor generally performs the tympanoplasty surgery through the ear canal.
In case, the ear canal is too narrow, the doctor will make an incision above or behind the ear to reach the eardrum.
The surgeon obtains a small piece of tissue called temporalis fascia to use as a graft or patch. Temporalis fascia is the connective tissue behind your ears near the temples.
The temporalis muscle is cut and placed under the hole in the eardrum to create a new intact ear drum. This tissue is called a graft.
Over time, your eardrum grows new tissue, using the graft material as the foundation.
What Are The Types Of Tympanoplasty?
Tympanoplasty can be classified into five types. (Wullstein classification)
Type I
Repair of the eardrum or the tympanic membrane only. In this case, the middle ear is normal. Type I tympanoplasty is similar to Myringoplasty.
Type II
Repair of the eardrum or the tympanic membrane and slight defects in the middle ear.
Type III
Involves repair of the eardrum or the tympanic membrane and the middle ear, when there are large defects of the malleus and incus. (Bones of the middle ear)
Type IV
The eardrum or the tympanic membrane is grafted onto the stapes footplate, which is movable.
Type V
Repair involves the stapes footplate, which is fixed.
Read our article on How the human ear works? To know the different parts and functions of our ear.
Perforated Eardrum Surgery Recovery Time
It generally takes a few weeks to fully recover from the eardrum surgery.
- Keep the operated ear dry, avoid showering for a few days, or cover the operated ear while showering.
- Slight blood is normal for a day or two after the surgery, consult your doctor if the bleeding continues.
- Do not blow your nose till it has completely healed.
- Sneeze with your mouth open.
- Avoid sports or any hectic physical activity for a few days.
- Mild pain is expected, use over-the-counter painkillers or as recommended by your surgeon.
Complications Of Tympanoplasty
- Ear surgery infection is the most common complication of tympanoplasty. Keep the operated ear dry. Read our article on how to prevent ear infections.
- Ringing in the ears or Tinnitus is another perforated eardrum surgery complication. Tinnitus may go away as the wound heals; in some cases, it is permanent.
- You may experience a change in taste, the feeling goes away gradually. In rare cases, it is permanent.
- Hearing should improve once the hole in the ear closes. In rare cases, there is not much improvement in hearing.
Tympanoplasty or eardrum surgery is relatively safe, studies report a success rate of 60 to 99% in adults and 35 to 94% in children.
if you have symptoms of a ruptured eardrum, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly. The majority of ruptured eardrums heal naturally, but severe cases may require surgery to repair the eardrum. Follow the doctor’s recommendations to avoid complications and promote healing.
References:
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
NHS UK
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK565863/
Tympanoplasty success rate



