Every hearing aid user knows a little about their listening device and often takes care of the small hearing aid problems or malfunctions to avoid a visit to the service center.
But how many of us know about the parts of the hearing aid and their functions? Or how the parts or the hearing aid components work? Every part of the hearing aid or the hearing aid component plays a very specific role. Which ultimately results in the clarity and pleasantness of the sound which we hear.
Let us get familiar with the hearing part names and their functions.
Hearing aid repairs are not advisable at home if one does not have the technical knowledge. But sorting out a few common hearing aid problems which do not involve opening the hearing aid are possible. Do read our blog on the handy tips to fix hearing aids at home.
What Are The Main Parts Of The Hearing Aid?
The main parts of the hearing aid are:
- The Hearing Aid Housing
- Ear Hook
- Hearing Aid Battery Compartment
- Buttons or Switches
- Earmolds
- Hearing Aid Microphone
- Hearing Aid Sound Processor
- Hearing Aid Amplifier
- Hearing Aid Receiver
- Wax Guards
The parts of the hearing aid can be divided into two groups. The visible external parts and the parts inside the housing or the shell. The hearing aid parts will differ depending on the type of hearing aids.
BTE, RIC, and Open Fit Hearing Aid Parts

In this blog, we will cover the parts of the hearing aid of Behind the Ear type of hearing aids, which include the RIC (Receiver in canal) type. Since they are the most popular hearing aids.
The Hearing Aid Housing
The BTE housing or body is mostly made of ABS (acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene) plastic. This thermoplastic has excellent stress and chemical resistance. Some brands coat the housing with water-resistant nano-coating.
What Is A Ear Hook?
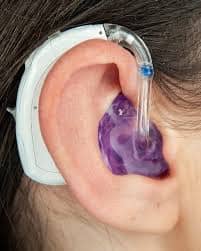
The BTE ear hook is a hollow tube molded in the shape of a hook, it’s made of silicone material and has two functions:
- To keep the hearing aid in place so the hearing does not fall off.
- To carry the sound from the Receiver or the speaker inside the housing to the earmold. The earmold is attached to the hook by a flexible silicon tube.
The Ear Hook Is Not A RIC Hearing Aid Part
The receiver or the speaker in the RIC hearing aid is outside the hearing aid. So, an ear hook or a tube is not required to carry the sound to the ear canal.
In the RIC hearing aid, the receiver though a part of the hearing aid is outside the body of the hearing aid attached by a set of wires. The receiver is directly inserted into the ear canal.
The RIC hearing aid comes with a set of soft domes of different sizes. The dome covers the receiver and slides into the ear canal for a perfect fit.
Hearing Aid Battery Compartment
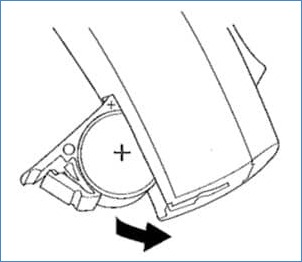
The hearing aid battery compartment or the battery drawer is primarily a tray that helps to slide the battery inside the hearing aid. On closing the tray, the battery makes contact with the metal contacts inside.
Earlier, it was just a battery compartment, but in the new digital hearing aids, it also serves as an On and Off switch. The latest hearing aids do not have a separate switch to shut down and switch on the hearing aid. Hearing aid users open or pull out the tray to shut down the hearing aid, and push the tray in to switch on the hearing aid.
What Do The Buttons On My Hearing Aid Do?
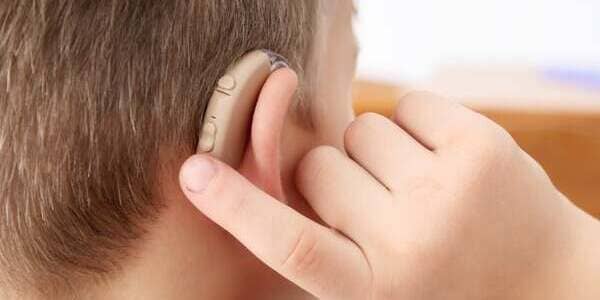
In most hearing aids the manufacturers provide two buttons or switches. The press button is the program change switch and the rocker switch is for increasing or decreasing the volume.
Digital hearing aids have multiple program settings. Depending on the situation and noise level around, the user changes the program to hear better.
What Are Earmolds?
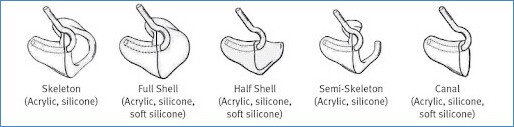
The earmold is a very important hearing aid accessory. The earmold is not supplied by the manufacturer as a part of the hearing aid. The audiologist or the fitting technician will provide the earmold. The earmold type will depend on the requirement of the hearing aid user.
A full shell hearing aid mold or a full concha mold is generally recommended if the user has a high hearing loss and the hearing aid output is high. A canal earmold is ideal for low to moderate hearing loss since the hearing aid output is not very high.
Hearing aid earmolds play a very important role. They cover the ear canal and prevent the sound from leaking out. This helps the user to hear well and also prevents acoustic feedback.
In case of high frequency hearing loss, a small opening called a vent allows the low frequency sound to escape. This improves the high frequency response.
Hearing aid molds tend to get blocked with earwax, read our blog on Hearing Aid home maintenance tips to avoid low sound output.
Parts Of The Hearing Aid – Internal
The internal parts or the electronic circuit and processors are responsible for the quality of the sound we ultimately hear. To know more about the working of hearing aids, read our blog on Analogue and Digital Hearing aids.
The hearing aid microphone is the first internal part of the hearing aid, it picks up the speech or sound. The job of the microphone is to pick up sound and convert the signals into electrical signals.
Where Is The Microphone On A Hearing Aid?

The location of the microphone is on the upper or outer facing part of the hearing aid body. Some hearing aids have more than one microphone, this helps in noise cancellation and a wider coverage area.
The microphone picks up the sound or speech and passes the electrical signal to the sound processor.
Hearing Aid Sound Processor
The hearing aid processor as the name implies processes the sound signal received from the microphone. The processor is a very important part of the hearing aid and is responsible for converting the analog signal into a digital signal.
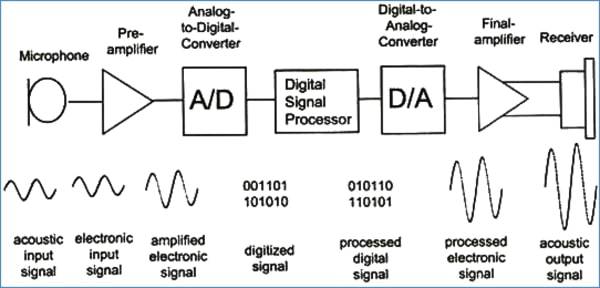
Hearing Aid Amplifier
The signal from the processor passes on to the amplifier. The Audiologist adjusts the output of the amplifier as per the requirement of the user.
Hearing Aid Receiver
The hearing aid receiver is a speaker or a transducer that produces the sound we finally hear.
How Does A Hearing Aid Receiver Work?
The hearing aid receiver converts the electrical signal received from the amplifier into sound waves or speech signals as we hear them. Hearing aids with more power have large receivers.
The location of the receiver in the conventional BTE hearing aid is at the base of the ear hook. In the RIC hearing aid, the receiver is outside the body of the hearing aid. The receiver covered with the dome slides into the ear canal as close to the eardrum as possible for better sound.
What Is A Wax Guard?
A wax guard is a small filter placed in the dome or earmold that prevents earwax from entering the hearing aid and damaging the receiver. This small part which is a fraction of the cost of a hearing aid plays a very important role.
Producing earwax is a natural process of the ear, some people produce more earwax which requires regular cleaning. (Check out how to clean earwax at home).
In a RIC hearing aid, the receiver is placed in the ear canal close to the eardrum. The soft earwax can block the sound outlet and may even damage the receiver if we do not use a wax guard.

To prevent this from happening, a small wax guard is placed at the tip of the dome. The wax guard prevents the wax from getting into the receiver and damaging it.
A wax guard is not required in a conventional BTE as the receiver is inside the body of the hearing aid and far from the earmold. The earmold can be easily removed and cleaned to avoid earwax blockage.
It is advisable to know the parts of the hearing aid. We can explain our problems to the audiologist or the technician to get a faster response in case of any performance issues.