The RPwD Act 2016 was enacted on 28.12.2016 which came into force from 19.04.2017.
The salient features of the RPwD Act 2016 are:
- Responsibility has been cast upon the appropriate governments to take effective measures to ensure that the persons with disabilities enjoy their rights equally with others.
- Disability has been defined based on an evolving and dynamic concept.
- The Act covers the following specified disabilities:
1. Physical Disability
A. Locomotor Disability
- Leprosy Cured Person
- Cerebral Palsy
- Dwarfism
- Muscular Dystrophy
- Acid Attack Victims
B. Visual Impairment
- Blindness
- Low Vision
C. Hearing Impairment
- Deaf
- Hard of Hearing
D. Speech and Language Disability
2. Intellectual Disability
- Specific Learning Disabilities
- Autism Spectrum Disorder
3. Mental Behaviour (Mental Illness)
4. Disability caused due to:
a. Chronic Neurological Conditions such as-
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Parkinson’s Disease
b. Blood Disorder-
- Haemophilia
- Thalassemia
- Sickle Cell Disease
Multiple Disabilities
- Additional benefits have been provided for persons with benchmark disabilities and those with high support needs.
- Every child with benchmark disability between the age group of 6 and 18 years shall have the right to free education.
- 5% reservation in seats in Government and Government aided higher educational institutions for persons with benchmark disabilities.
- Stress has been given to ensure accessibility in public buildings (both Government and private) in a prescribed time-frame.
- 4% reservation in Government jobs for certain persons or class of persons with benchmark disability.
- The Act provides for grant of guardianship by District Court or any authority designated by the State Government under which there will be joint decision – making between the guardian and the persons with disabilities.
- Broad based Central & State Advisory Boards on Disability to be set up as policy making bodies.
- The Act provides for strengthening of the Office of Chief Commissioner of Persons with Disabilities and State Commissioners of Disabilities which will act as regulatory bodies and Grievance Redressal agencies and also monitor implementation of the Act. These Offices will be assisted by an Advisory Committee comprising of experts in various disabilities.
- Creation of National and State Fund to provide financial support to the persons with disabilities.
- The Act provides for penalties for offences committed against persons with disabilities.
- Designated special Courts to handle cases concerning violation of rights of PwDs.
Click on the link to request for a copy of the complete RPwD act 2016 (Rights of persons with disabilities act 2016). The RPwD act 2016 pdf copy will be emailed to you.
The Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment, Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities have framed guidelines for the purpose of assessing the extent of specified disability in a person included under the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act 2016 (RPwD act 2016)
Read more about the guidelines for applying for the Disability Card or UDID card online in our article on Guidelines for Issue of Hearing Disability Certificate.
Reference: Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (Divyangan)
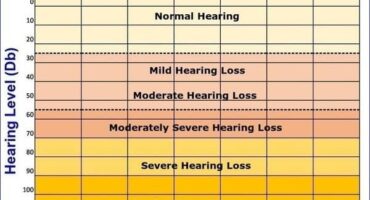



There are 4% who have reservation rights, and I have 56% hearing loss am I entitled to government job reservation or not?
Should 56% hearing loss or 75% above hearing loss be eligible for government job reservation?
As per the qualifying rules, the person should have 60% hearing loss.